Dear colleagues,
It is a pleasure to announce that a new scientific paper has been published on the Focus Point : "New Technologies for Detection, Protection, Decontamination and Developments of the Decision Support Systems in Case of CBRNe Events" that one of the 3 the special issue of SICC Series - CBRNe Conference 2020 published on the European Physics Journal Plus.
link: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01771-8
Abstract:
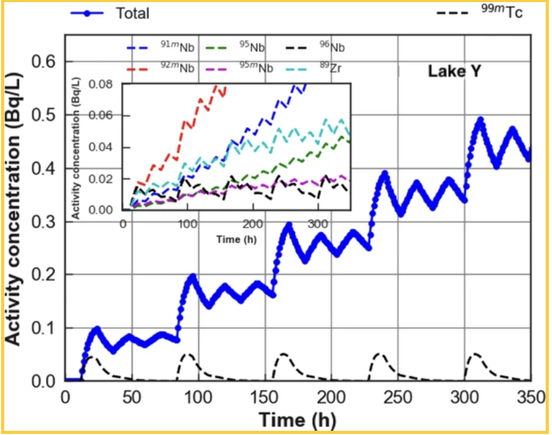
The aim of the present study is to model mixing and transport of radioactive effluents in the course of time between two water reservoirs. To test the model, a hypothetical case study is presented of liquid effluents potentially released during normal operation of a fusion neutron source devoted to radioisotopes production. A suitable example is an accelerator-driven intense D-T 14 MeV neutron source relying on T and D ion beams, with the potential to provide a neutron yield in the range 5−7⋅10E13 s-1. It is expected that during normal operation a number of radionuclides will be produced and managed. The present report discusses the mechanisms and parameters which affect and control the fate of radionuclides potentially released into two connected water reservoirs during normal operation of the plant. A mathematical mixing model is developed that describes groundwater flow and radioactive transport between the two basins. The aim of this study is to estimate the amount of radioactivity concentration in both water reservoirs at any time, an information that can be used for radiation protection purposes.

Write a comment